How to Interpret Complex Hearing Test Results
Getting your hearing tested can feel like stepping into unfamiliar
Getting your hearing tested can feel like stepping into unfamiliar
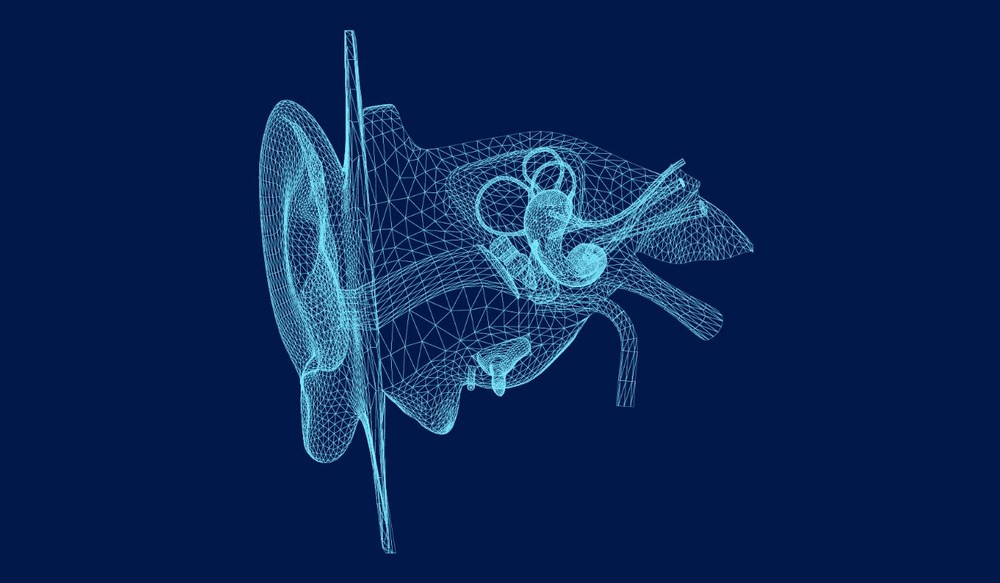
Your inner ear manages both hearing and balance, using the same small

Adapting to changes in hearing can take time, and it’s not uncommon for